New study reveals soil health benefits of regenerative agriculture
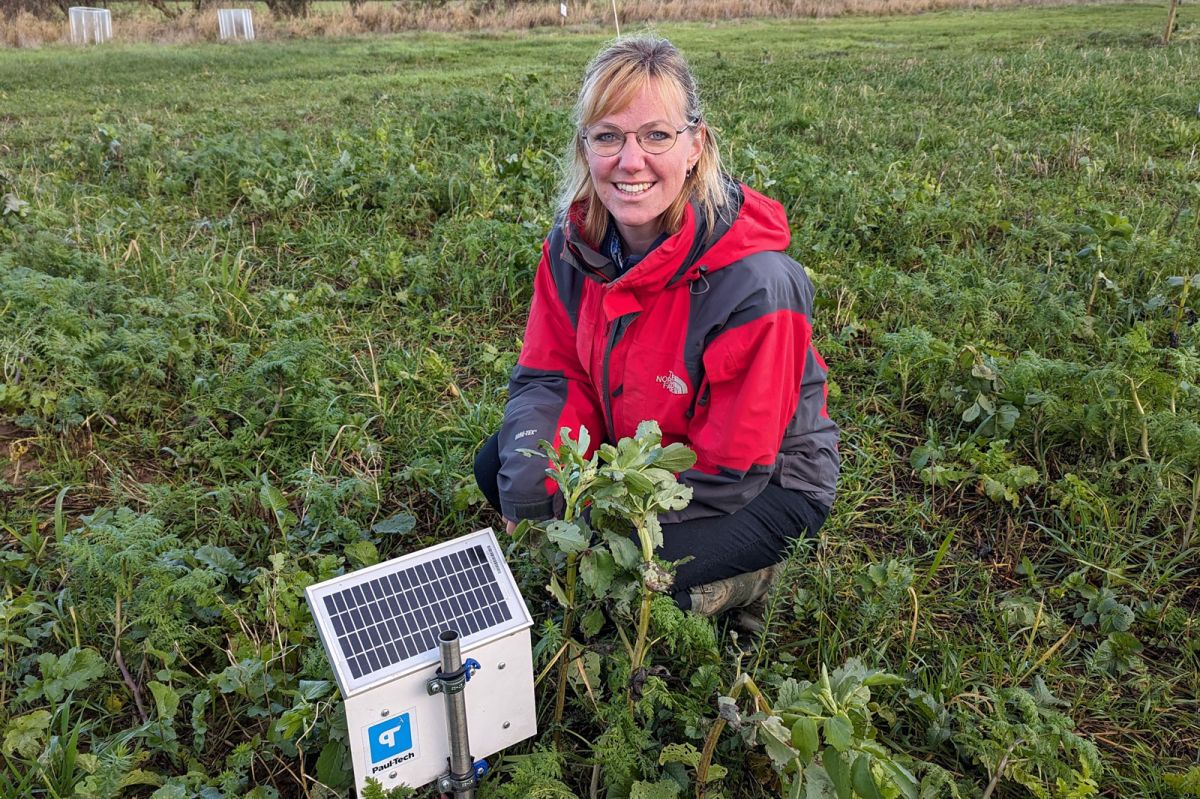

The study compares soil health, crop production, greenhouse gas emissions, and profit of different farming systems across seven 12m x 40m plots. Some of the plots were ploughed and power harrowed, while others underwent minimal cultivation using non-inversion, shallow cultivation.
Cover cropping, living mulches, manures, livestock integration, and herbal leys have also been utilised as part of the trial. Data were collected by state-of-the-art soil stations created by Estonian ag-tech company Paul-Tech, which take real-time readings of nutrient availability, soil water levels and soil temperature at depths of 8cm and 20cm.
Each plot received three treatments of nitrogen throughout the trial, with nutrient and water availability measured at both depths after each application. The stations revealed that the trial plots which had minimal cultivation held more nutrients and water around the root zone for longer than plots that had been ploughed.
As a result, the minimal cultivated plots recorded a significantly larger nutrient release after fertilisation and higher nutrient availability at the 8cm mark compared to the ploughed plots, and nutrients were held around the rootzone for longer.
By contrast, water quickly drained through the ploughed soil, leading to a significantly smaller nutrient release at fertilisation and considerably less nutrients available to the plants at 8cm.
Soil temperature was also impacted by the cultivation method with the ploughed soil experiencing much larger temperature changes over the course of the trial.
The ploughed soil froze when air temperatures dipped below zero, whereas those sown under a minimal cultivation system maintained a much more stable temperature throughout and did not freeze.
Commenting on the study findings, Paul-Tech chief executive, Mikk Plakk, described them as ‘fascinating’. The study is ongoing and will look at the impacts of other regenerative techniques on soil health over a longer period.
He said: “The findings have a significant bearing on how farmers should be treating soil. They strongly suggest cultivation methods have the potential to significantly improve soil and plant health while reducing the amount of inputs they need to apply.”
Paul Tech’s soil station combines real-time proprietary sensor data with weather and satellite data to produce agronomic recommendations for farmers and growers, which are reported via an online dashboard. This empowers them to make more informed decisions about crop inputs and irrigation, leading to better soil health, plant health, yield and cost savings.
The trial is being led by Dr Ruth Wade, research fellow at the University of Leeds. She said: “The results coming from this regenerative agriculture plot trial will provide important data on the impacts of different farming systems both on the environment but also for the farm business.”
The system is in place on commercial farming operations in Scandinavia and Eastern Europe and is being launched in the UK this month. Paul-Tech’s soil system will see its official UK launch at LAMMA on January 17-18 at Birmingham’s NEC.